Publications

Retrotope presented data demonstrating arrest of disease progression with treatment of RT001 in patients with Infantile Neuroaxonal Dystrophy (INAD) The data were presented at the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD), Rare Diseases & Orphan Products Breakthrough Summit® on October 15-16, 2018, in Washington, D.C.
Read more
RT001 is a deuterated ethyl linoleate that inhibits lipid peroxidation and is hypothesized to reduce cellular damage and recover mitochondrial function in degenerative diseases such as Friedreich's ataxia.
Read more
INAD is an ultra-rare inherited neurological disorder. It begins within the first few years of life, and leads to a progressive impairment of movement, cognition, and vision. Its prevalence is extremely rare (<1:200,000), and it is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
Read more
Strong correlations among four measures of disease progression in Friedreich's ataxia
Read more

Alzheimer's disease (AD) involves progressive deposition of amyloid β-peptide (Aβ), synapse loss, and neuronal death, which occur in brain regions critical for learning and memory.
Read more

Lipoxygenases (LOXs) have been implicated as central players in ferroptosis, a recently characterized cell death modality associated with the accumulation of lipid hydroperoxides: the products of LOX catalysis.
Read more
Arachidonic acid (AA, 20:4) is an omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) and the main precursor to the class of lipid mediators known as eicosanoids.
Read more

Selective deuteration of drugs and biologically relevant molecules is becoming increasingly important in the pharmaceutical industry.
Read more
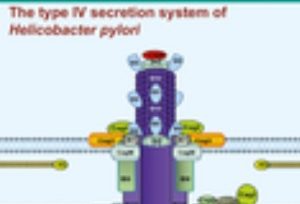
Oxidative damage due to increased oxidative stress is considered an important factor in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative diseases including retinal diseases, Parkinson's disease (PD), and Huntington's disease.
Read more

With the permission of McGraw Hill, a pre-publication copy of Chapter 13 from "Get to Aha! Discover Your Corporate DNA to Dominate the Competition" by Andy Cunningham.
What could be better than being part of the Next Big Thing? Who wouldn’t want to have a piece of a Next Big Thing company—an Apple Amazon, Google, Netflix, or Salesforce—right on the cusp of takeoff?
Read more
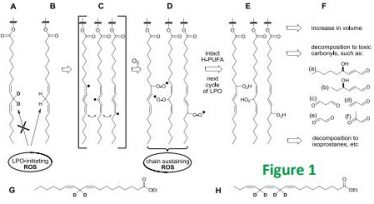
LPO generates multiple types of damage, from deteriorating membrane properties to various toxic and/or signaling compounds. D-PUFAs, even at low concentrations, inhibit the LPO.
Read more

Deuteration at bis‐allylic positions slows down hydrogen abstraction, thereby reducing the rate of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) oxidation.
Read more