Isotope-Reinforced Polyunsaturated Lipids (D-PUFA) Mitigate Symptoms in Diverse Alzheimer’s Mouse Models
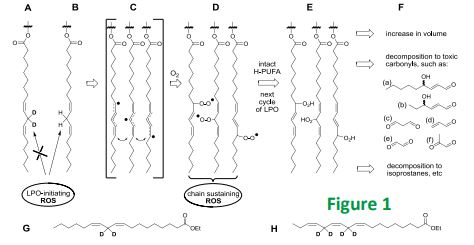
LPO generates multiple types of damage, from deteriorating membrane properties to various toxic and/or signaling compounds. D-PUFAs, even at low concentrations, inhibit the LPO.
Diets were based on 12% fat AIN93M. The fat fraction included saturated;monounsaturated fats;and 10% PUFAs (1:1ratio) of either H-Lin
and H-Lnn (control),or D2 -Lin and D4 -Lnn (drug). Mice had ad libitum access to food and water.All mice were housed with a 12h light/dark
cycle. Deuterium incorporation was monitored by irMS, reaching DPUFA incorporation levels necessary to inhibit the LPO.
55 male APP/PS1 or C57Bl6 mice were fed D-PUFA or H-PUFA diets for 5 months starting at 4-7 MO. No difference was observed between D- and H-cohorts in the behavioural tests. While in cortex various Aβ species were at the same level for D- and H-diets, there was a substantial decrease in hippocampus in the D-group.
